Critical Langchain Vulnerability Allows Hackers to Steal Confidential Information from AI Systems

Critical Langchain Vulnerability Allows Hackers to Steal Confidential Information from AI Systems
Through deserialization problems, a significant vulnerability in LangChain’s core library (CVE-2025-68664) enables attackers to exfiltrate important environment variables and perhaps run code.
The problem, which was found by a Cyata researcher and fixed shortly before Christmas 2025, impacts one of the most widely used AI frameworks with hundreds of millions of downloads.
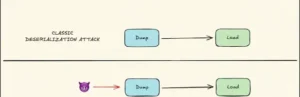
The dumps() and dumpd() functions of LangChain-core were unable to get past user-controlled dictionaries that had the reserved “lc” key, which designates internal serialized objects.
This resulted in serialization-deserialization cycles in typical flows like event streaming, logging, and caching, which caused deserialization of untrusted data (CWE-502) when LLM outputs or prompt injections affected fields like additional_kwargs or response_metadata. Twelve susceptible patterns were found, including astream_events(v1) and Runnable.astream_log(), with a CNA-assigned CVSS score of 9.3, rating it Critical.
During audits of AI trust boundaries, a Cyata security researcher discovered the vulnerability by tracking deserialization sinks and identifying the missing escape in serialization code.
It was reported via Huntr on December 4, 2025, and LangChain published the advisory on December 24 after acknowledging it the next day. Langchain-core versions 0.3.81 and 1.2.5 include patches that wrap dicts containing “lc” and deactivate secrets_from_env by default, which was previously enabled and allowed direct env var leaks. A record $4,000 bounty was given out by the team.
Using environment variables in headers for exfiltration, attackers might create prompts to instantiate allowlisted classes, such as ChatBedrockConverse, from langchain_aws, resulting in SSRF.
If PromptTemplate is used after deserialization, Jinja2 rendering is enabled for potential RCE. The scale of LangChain increases risk: Last month, pypistats recorded over 98 million downloads, whereas pepy.Tech recorded about 847 million.
Verify dependencies such as langchain-community and update langchain-core right away. Disable secret resolution until inputs are validated, audit deserialization in streaming and logs, and treat LLM outputs as untrusted. A parallel vulnerability in LangChainJS (CVE-2025-68665) highlights the dangers of agentic AI plumbing.
Amidst the rapid uptake of LLM apps, organizations need to inventory agent deployments for quick triage.
About The Author:
Yogesh Naager is a content marketer who specializes in the cybersecurity and B2B space. Besides writing for the News4Hackers blogs, he also writes for brands including Craw Security, Bytecode Security, and NASSCOM.
Read More:
A New Cyber Trap “Fake e-Challan Links”: Reasons to Stay Alert