WHO Reports Details Responses to Cyberattacks Against Healthcare and the Growth of Misinformation during Public Health Emergencies.

WHO Reports Details Responses to Cyberattacks Against Healthcare and the Growth of Misinformation during Public Health Emergencies.
Although digital tools have provided new avenues for improving health and well-being, they have also introduced novel health security vulnerabilities, such as cyber-attacks on healthcare systems and the spread of disinformation. In order to enhance comprehension of these hazards and mitigate their probability and magnitude, the World Health Organization (WHO) generated two reports in partnership with INTERPOL, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), the UN Office of Counter-terrorism, the UN International Computing Centre (UNICC), the UN Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute, and the CyberPeace Institute.

The two papers, published on 26 January 2024, outline strategies to enhance health security through practical measures.
The initial paper, titled “Analyzing the peril of cyber-attacks on health care amidst the COVID-19 pandemic,” underscores the extensive tangible consequences of cyber-attacks on the healthcare sector. Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a growing focus on cyber-attacks targeting health information technology (IT) infrastructure. These attacks often impeded hospitals from providing prompt and essential care during critical periods. Healthcare facilities made significant ransom payments in order to repair their IT systems and recover stolen data. These cyber-attacks prompted law enforcement agencies to issue warnings regarding the possibility of cyber-attacks against the health industry.
Cybercrime, in all its manifestations, is continuously developing and expanding. “The COVID-19 pandemic brought this into clear view,” stated Glen Prichard, the Chief of the Cybercrime and Anti-Money Laundering division at UNODC. The research emphasizes the susceptibility of patient safety to cyberattacks and underscores the significant effort required to safeguard lives.

Healthcare systems worldwide have adopted digital technology to improve the clinical quality and cost-effectiveness of their services. This phenomenon has resulted in a reliance on digital technology, which has progressed, at times without thorough evaluation of emerging threats and adequate allocation of resources towards safeguarding against cyber attacks. The presence of sensitive data within health services, along with insufficient security measures, renders healthcare infrastructure highly susceptible to cybercriminal attacks.
“This report serves as a clarion call,” stated Sameer Chauhan, Director of UNICC. UNICC serves as the main provider of shared cybersecurity services to the UN system, actively defending our UN community from advanced cyber-attacks. We appreciate the recommendation from WHO for Member States to enhance cybersecurity in the healthcare industry by utilizing shared cybersecurity capabilities, such as the shared threat intelligence and cybersecurity resources provided by UNICC for the UN system. We are prepared and enthusiastic to provide them with guidance in this matter.

In order to mitigate the increasing digital threats to the healthcare sector, it is crucial to bolster cyber-maturity. Cybersecurity maturity refers to the preparedness of an organization to protect itself and its digital assets against cyber-attacks. This entails allocating resources to individuals, procedures, and technology, which includes providing cyber-awareness training and creating incident response plans that will be practiced by employees in preparation for a cyber-attack. Enhancing communication and collaboration with law enforcement agencies (such as police and INTERPOL), governmental agencies (including cyber-security agencies, public health institutes, national agencies for the safety of medicines and health products, and nuclear safety agencies), private sector, and non-governmental organizations is crucial. These entities can offer timely alerts and warnings regarding ongoing cyber-attacks.
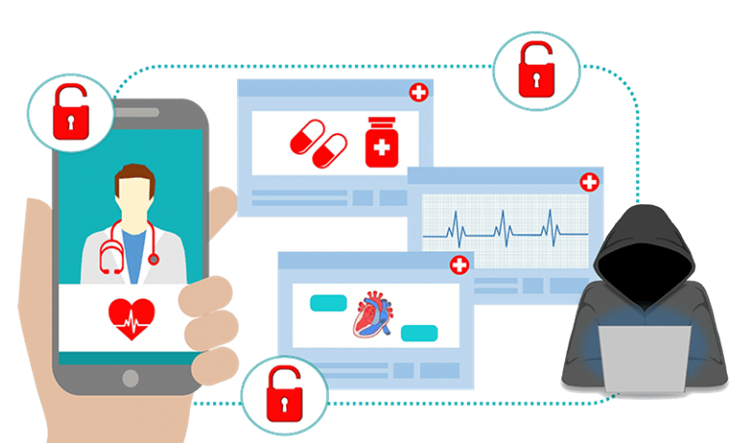
The second report, titled “Understanding Disinformation in the Context of Public Health Emergencies: The Case of COVID-19,” examines various strategies for combating disinformation. Disinformation, in contrast to misinformation, is deliberately generated with the malevolent purpose of instigating conflict, disharmony, and distrust towards specific targets, including government agencies, scientific experts, public health agencies, the commercial sector, and law enforcement. Disinformation can be described as the deliberate manipulation and weaponization of information.

Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the historical context of infectious disease deception and its relationship with public health is essential for developing effective strategies to combat disinformation. The report analyzes several forms of pandemic disinformation over a period of time, as well as the ways in which criminals manipulate the cognitive processes of the audience. In order to tackle the hazards posed by professionally created and widely spread misinformation campaigns, which may be driven by a broader and long-term ideological or political objective, or for economic benefit, it is necessary for WHO and public health partners to employ multi-faceted tactics.

The report suggests a variety of strategies to combat disinformation:
- Increasing awareness of deception and manipulation of information; Advocating for the development of critical thinking skills;
- Advocating for initiatives that enhance knowledge and understanding in the areas of digital technology, health, and scientific concepts;
- Advocating for reliable sources of information and authoritative voices;
- Providing assistance to fact-checking endeavors that involve the utilization of fact-checking technologies and human fact-checkers;
- Collaborating with pertinent parties, including the security sector, social media providers, law enforcement, cyber agencies, NGOs, and international organizations, to address this emerging issue, and
- Examining the factors that contribute to the presence of trust or mistrust among people, and how these factors are used to develop campaigns spreading false information. These drivers can provide valuable insights for developing enduring strategies to combat deception. When confronted with novel information, it is imperative for individuals to inquire within themselves:
- Can this content be considered dependable?
- What is the author’s identity?
- Where have the assertions been made?
- Is the source of information trustworthy?
- What emotions do I have regarding this information?

The studies provide a valid rationale for establishing partnerships across several sectors, which can effectively leverage the advantages of new technology to enhance health and well-being, while simultaneously addressing the ongoing emergence of dangers.
About The Author:
Yogesh Naager is a content marketer who specializes in the cybersecurity and B2B space. Besides writing for the News4Hackers blog, he’s also written for brands including CollegeDunia, Utsav Fashion, and NASSCOM. Naager entered the field of content in an unusual way. He began his career as an insurance sales executive, where he developed an interest in simplifying difficult concepts. He also combines this interest with a love of narrative, which makes him a good writer in the cybersecurity field. In the bottom line, he frequently writes for Craw Security
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE
Aadhaar Card Fraud: Are Aadhaar Cards Given At The Time of Hotel Booking? Your Bank Account May Gone Empty
5 Apprehended for Deceiving A Woman in Hyderabad of ₹3 Crore in A Trading Fraud
A Romance Scam Patchwork Lures To Infect Android Devices with the VajraSpy Malware






