Exploring Malware Threats: A Vital Component of CEH Module

Exploring Malware Threats
Exploring Malware Threats: A Vital Component of CEH Module
In the realm of cybersecurity, understanding malware threats is paramount. Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a diverse range of software designed to infiltrate, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. In the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) module, comprehensive knowledge of malware threats forms a critical foundation for safeguarding digital assets and networks. This article delves into the significance of malware threats within the CEH framework, highlighting key types of malware and strategies for mitigation.
Understanding Malware:

Malware manifests in various forms, each posing unique challenges to cybersecurity professionals. Among the prominent types of malware are viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and rootkits. Viruses attach themselves to legitimate programs and replicate when those programs are executed, spreading across systems. Worms, on the other hand, self-replicate and spread independently, exploiting vulnerabilities in network protocols. Trojans disguise themselves as benign software to deceive users into executing them, granting attackers unauthorized access to systems. Ransomware encrypts files or locks systems, demanding ransom payments for decryption or restoration. Spyware covertly gathers sensitive information, while adware inundates users with unwanted advertisements. Rootkits conceal malicious activities by modifying system functions and evading detection.
Significance in CEH Module:
In the CEH module, understanding malware threats is indispensable for several reasons. Firstly, it enables ethical hackers to recognize and analyze malicious code, facilitating the identification of vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors. By comprehending the characteristics and behaviors of different malware types, CEH professionals can develop effective countermeasures and mitigation strategies. Moreover, familiarity with malware aids in the implementation of proactive security measures, including intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and antivirus software. Ethical hackers equipped with robust knowledge of malware threats can simulate real-world attack scenarios, allowing organizations to fortify their defenses and preemptively address vulnerabilities.
Mitigation Strategies:
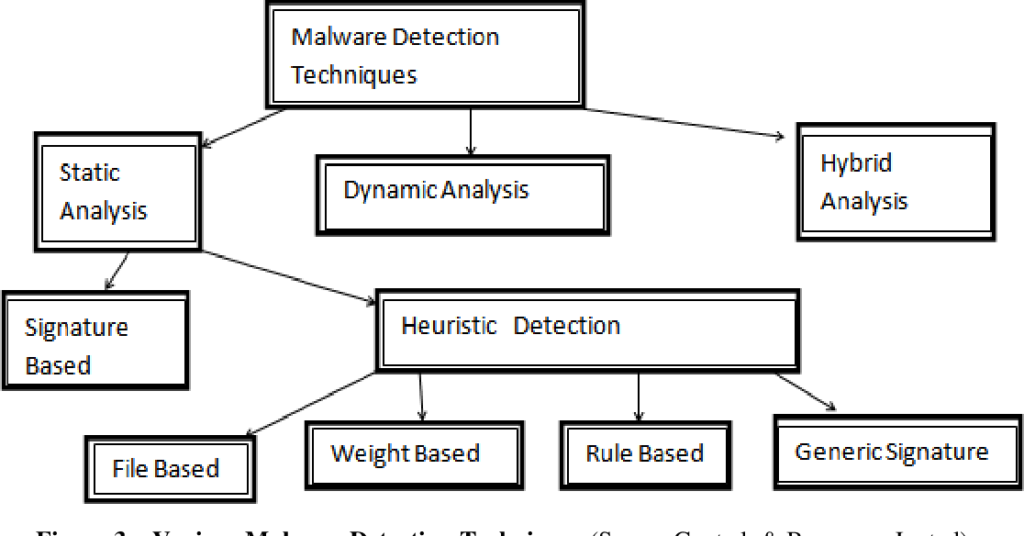
Mitigating malware threats demands a multifaceted approach encompassing prevention, detection, and response strategies. Proactive measures such as regular software updates, patch management, and employee training play a pivotal role in thwarting malware attacks. Network segmentation and access controls restrict the lateral movement of malware within organizational networks, limiting the scope of potential breaches. Intrusion detection systems and behavior-based analytics enable early detection of malicious activities, allowing for timely intervention and containment. In the event of a malware incident, swift incident response protocols, including containment, eradication, and recovery procedures, are imperative to minimize damage and restore normal operations.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, malware threats remain a persistent and evolving menace. Within the CEH module, a comprehensive understanding of malware is indispensable for ethical hackers tasked with safeguarding digital assets and networks. By familiarizing themselves with various types of malware and adopting proactive mitigation strategies, cybersecurity professionals can effectively defend against malicious attacks and mitigate potential risks. As organizations confront increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, the integration of robust malware defense mechanisms within the CEH framework is essential to ensure resilience and protect against emerging vulnerabilities.
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE