How to get sensitive data from Google

How to get sensitive data from Google
The Google Hacking Database (GHDB) is an abstract of Google hacking search terms that have been found to uncover touchy information uncovered by weak workers and web applications. The GHDB was dispatched in 2000 by Johnny Long to serve infiltration analyzers. … Documents with touchy information, passwords, and usernames.

In 2010, Long gave the database to Offensive Security and it turned out to be essential for exploit-db.com. It was likewise extended to incorporate the Google internet searcher as well as other web indexes like Microsoft’s Bing just as different stores like GitHub.
We can hack sites by google?
You can’t hack sites straightforwardly utilizing Google. Be that as it may, its enormous web creeping capacities can be of extraordinary assistance to record nearly anything inside any site which incorporates delicate data. This can incorporate username, secret phrase, and other general weaknesses you will not be knowing.
Google Dorking is a strategy utilized by hackers to discover the data which is presented inadvertently to the web. For instance, log records with usernames and passwords or cameras and so forth. It is done generally by utilizing the questions to pursue a particular objective slowly.
Some useful google dorks
Cache: In the event that you remember different words for the question, Google will feature those words inside the cached archive. For example, [cache:www.google.com web] will show the cached content with “web” featured. This usefulness is likewise open by clicking on the “Cached” connect on Google’s primary outcomes page. The inquiry [cache:] will show the variant of the page that Google has in its cache. For example, [cache:www.google.com] will show Google’s cache of the Google landing page. Note there can be no space between the “cache:” and the page URL.
Link: The inquiry [link:] will list pages that have connections to the predetermined site page. For example, [link:www.google.com] will list site pages that have joined highlighting the Google landing page. Note there can be no space between the “interface:” and the page URL.
Related: The question [related:] will list website pages that are “comparable” to a predetermined page. For example, [related:www.google.com] will list website pages that are like the Google landing page. Note there can be no space between the “related:” and the website page URL.
Inurl: On the off chance that you incorporate [inurl:] in your question, Google will limit the outcomes to archives containing that word in the URL. For example, [inurl: google search] will return archives that notice “google” in their URL, and notice “search” anyplace in the record (URL or no). Note there can be no space between the “inurl:” and the accompanying word. Putting “inurl:” before each word in your query is identical to putting “allinurl:” at the front of your question: inurl: google inurl: search] is equivalent to [allinurl: google search].
Site: On the off chance that you incorporate [site:] in your question, Google will limit the outcomes to those websites in the given space. For example, [help site:www.google.com] will discover pages about help inside www.google.com. [help site:com] will discover pages about help inside .com URLs. Note there can be no space between the “site:” and the area.
Filetype: This administrator trains Google to look just inside the content of a specific kind of record. This administrator requires an extra pursuit contention. The “filetype” administrator doesn’t perceive various renditions of the equivalent or comparable organizations (for example doc versus Docx, Xls versus xlsx versus CSV), so every one of these arrangements should be dorked independently. used to look for any sort of document augmentations, for instance, assuming you need to look for pdf records you can utilize.
Info: The inquiry [info:] will introduce some information that Google has about that website page. For example, [info:www.google.com] will show information about the Google landing page. Note there can be no space between the “info:” and the site page URL.
Intitle : In the event that you incorporate [intitle:] in your question, Google will confine the outcomes to archives containing that word in the title. For example, [intitle: google search] will return records that notice “google” in their title, and notice “search” anyplace in the report (title or no). Note there can be no space between the “intitle:” and the accompanying word. Putting [intitle:] before each word in your question is comparable to putting [allintitle:] at the front of your query: [intitle:google intitle:search] is equivalent to [allintitle: Admin Login].
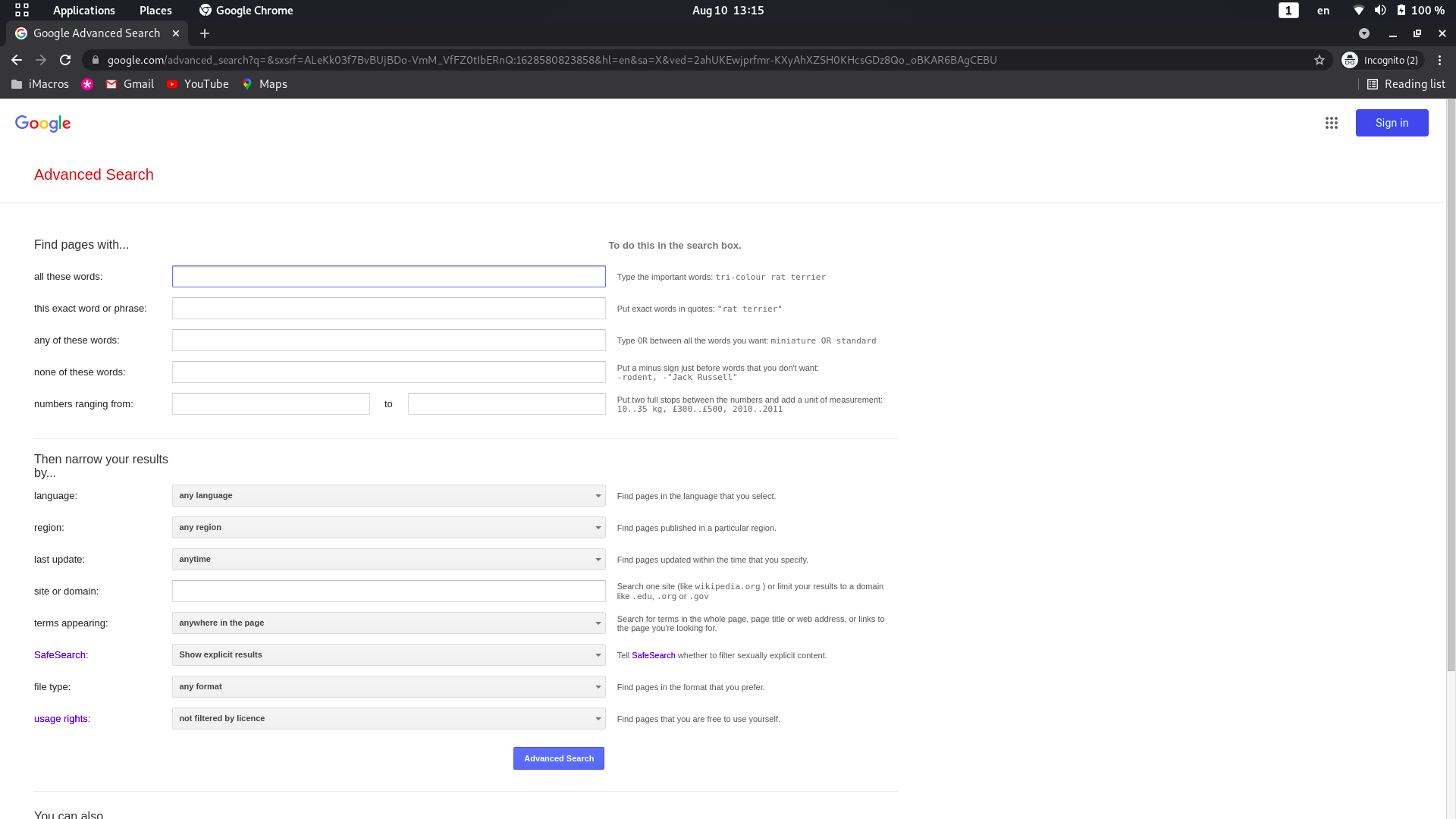
How to use google advanced search for better searching
Step 1: On your computer, go to google.com.
Step 2: Do a search.

Step 3: Choose the type of results: All, Images, Videos, or Books.
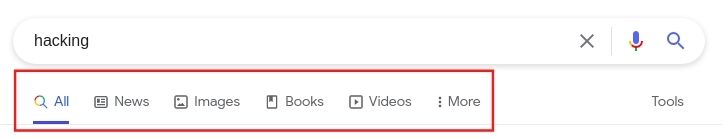
Step 4: click on the tool

Step 5: customized result by time and result
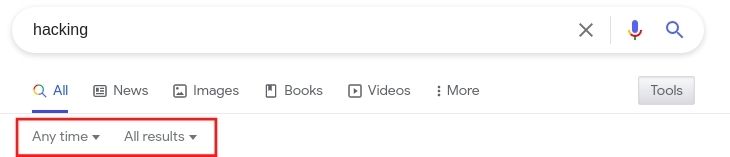
Step 6: Click Settings and then Advanced search.