Network Scanning

Network Scanning
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber security, the role of Certified Ethical Hackers (CEH) is paramount. Armed with specialized knowledge and skills, these professionals are entrusted with the task of safeguarding digital assets by identifying and mitigating potential vulnerabilities. The Certified Ethical Hacker v12 certification program equips individuals with the expertise needed to navigate the intricate realm of ethical hacking responsibly and effectively.

Module Overview:
One of the cornerstone modules within the CEH v12 curriculum is the Scanning module. Scanning serves as a crucial phase in the ethical hacking process, allowing practitioners to assess the security posture of target systems comprehensively. Through a series of methodologies and techniques, ethical hackers gain insights into the vulnerabilities present within a network or system, laying the groundwork for further analysis and remediation.
Understanding Scanning:
Scanning encompasses a diverse array of activities aimed at gathering information about target systems, identifying open ports, services, and potential entry points for exploitation. Ethical hackers leverage an arsenal of scanning tools and methodologies to conduct thorough assessments, including:

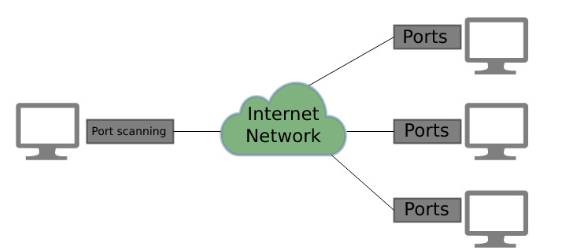
Port Scanning: Ethical hackers utilize port scanning techniques to identify open ports and services running on target systems. By probing network endpoints, they can pinpoint potential entry points for unauthorized access or exploitation.
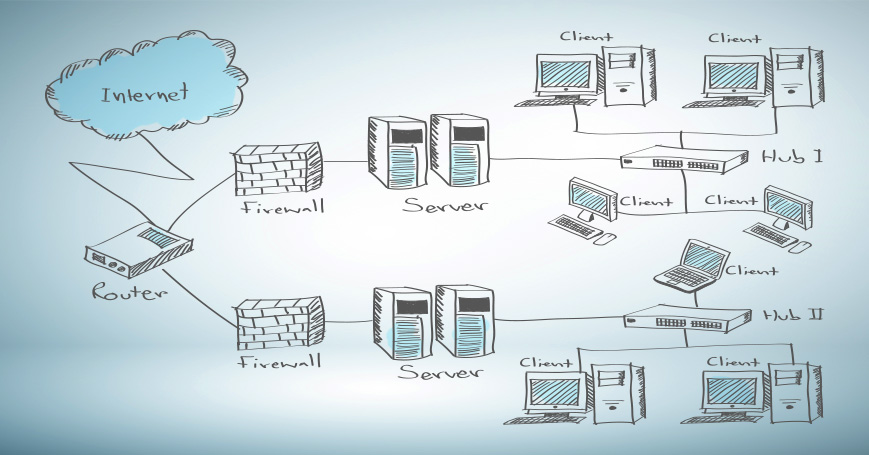
Network Mapping: Network mapping involves creating a visual representation of the target network’s infrastructure, including interconnected devices, routers, and switches. This process provides valuable insights into network topology, aiding ethical hackers in understanding the scope and complexity of the environment under assessment.
Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning involves the automated detection of known vulnerabilities within target systems or applications. Ethical hackers leverage specialized tools to scan for security weaknesses, Misconfigurations, and outdated software versions, enabling proactive risk mitigation measures.

Banner Grabbing: Banner grabbing entails extracting information from network services, such as web servers or FTP servers, to ascertain version details and configuration parameters. This information assists ethical hackers in identifying potential attack vectors and crafting tailored exploits.
Enumeration: Enumeration involves the systematic extraction of valuable information from target systems, including user accounts, network shares, and system configurations. Ethical hackers leverage enumeration techniques to gather intelligence and identify potential avenues for privilege escalation or lateral movement.
Best Practices and Ethical Considerations:

While scanning is an essential component of the ethical hacking process, it is imperative for practitioners to adhere to ethical guidelines and legal frameworks. Ethical hackers must obtain proper authorization before conducting any scanning activities and ensure that their assessments do not cause disruption or harm to target systems. Additionally, thorough documentation and reporting of findings are essential to facilitate informed decision-making and remediation efforts.
Conclusion:
The Scanning module within the Certified Ethical Hacker v12 curriculum equips aspiring ethical hackers with the knowledge and skills needed to conduct comprehensive assessments of target systems effectively. By mastering the art of scanning, practitioners can identify vulnerabilities, assess security risks, and contribute to the ongoing effort of safeguarding digital assets in an increasingly interconnected world. As ethical hacking continues to play a pivotal role in cyber security, the importance of continuous learning and adherence to ethical principles cannot be overstated.
We Have Some Tools of Scanning
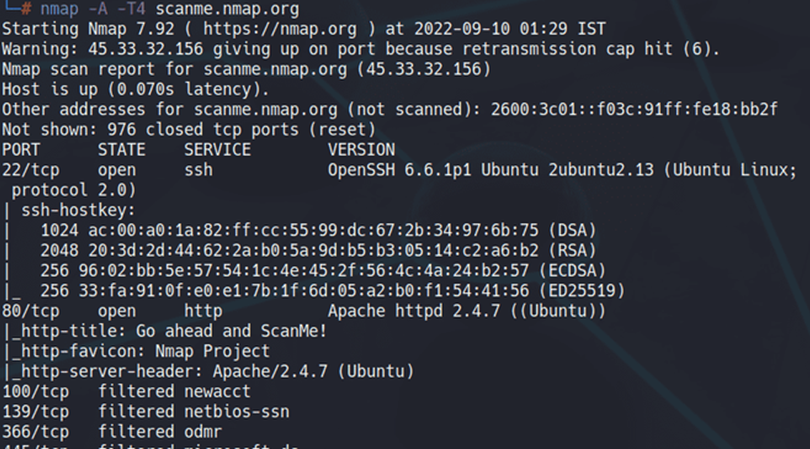
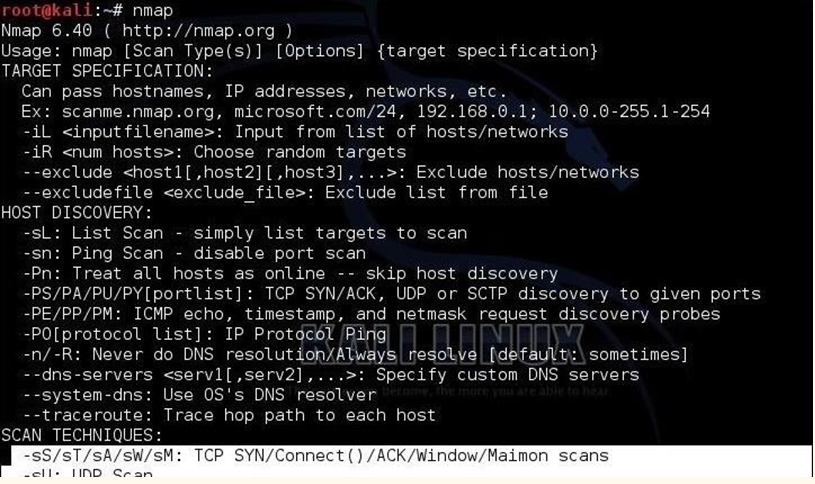
Nmap (Network Mapper):
Command: nmap [target]
Description: Nmap is a powerful open-source network scanning tool used for discovering hosts and services on a computer network.
Wireshark:
Command: wireshark
Description: Wireshark is a popular network protocol analyzer that allows for packet capturing, network troubleshooting, and analysis.
Angry IP Scanner:
Command: ipscan
Description: Angry IP Scanner is a lightweight and fast IP address and port scanner.
Masscan:
Command: masscan [target]
Description: Masscan is an ultra-fast TCP port scanner capable of scanning the entire Internet in under 6 minutes.
Masscan
OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System):
Command: openvas
Description: OpenVAS is an open-source vulnerability scanner that detects security issues in networks.
Zenmap (Nmap GUI):
Command: zenmap
Description: Zenmap is the official graphical user interface (GUI) for Nmap, providing an easy-to-use interface for Nmap scanning.
Netcat (nc):
Command: nc [options] [target] [port]
Description: Netcat is a versatile networking utility for reading and writing data across network connections.
Please note that these tools should be used responsibly and ethically, with proper authorization, as unauthorized scanning can be illegal and unethical. Additionally, the commands provided are basic examples; each tool has a wide range of options and capabilities beyond what’s listed here.
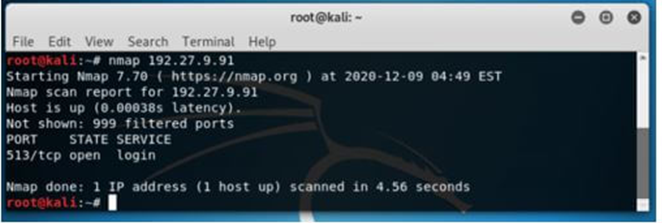
Eg Nmap
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE
Kali Linux Tutorial for Beginners: What is, How to Install & Use
Ethical Hacking Techniques and the Perfect Tools
Top 10 Cybersecurity Software To Use in 2024