Kali Linux Tutorial for Beginners: What is, How to Install & Use

Kali Linux Tutorial for Beginners: What is, How to Install & Use
What is Kali Linux?
Kali Linux is a security variant of Linux that was created especially for advanced penetration testing and computer forensics. It is derived from Debian. Moreover, it was created by Offensive Security’s Mati Aharoni and Devon Kearns reworking BackTrack.
Several well-crafted tools for a range of information security tasks, including computer forensics, penetration testing, security research, and reverse engineering, are included in Kali Linux. Their prior information security operating system was called BackTrack.
Introduced in March 2013, Kali 1.0.0 was the initial version of Kali Linux. Kalin Linux is being sponsored and maintained by Offensive Security. “Our Most Advanced Penetration Testing Distribution, Ever” is a giant banner that can be seen if you visit Kali’s website nowadays (www.kali.org).
An extremely bold claim that, ironically, hasn’t been refuted yet. There are more than 600 preconfigured penetration-testing apps on Kali Linux for you to explore. Every software has a different use case and degree of flexibility. These helpful tools are expertly divided into the following categories by Kali Linux:
- Information Gathering
- Vulnerability Analysis
- Wireless Attacks
- Web Applications
- Exploitation Tools
- Stress Testing
- Forensics Tools
- Sniffing & Spoofing
- Password Attacks
- Maintaining Access
- Reverse Engineering
- Reporting Tools
- Hardware Hacking
Who uses Kali Linux and Why?
Being one of the rare operating systems that both good folks and bad guys freely utilize, Kali Linux is an unusual operating system. This operating system is heavily used by both Black Hat Hackers and Security Administrators.
One is responsible for identifying and stopping security breaches, while the other may find and take advantage of them. Because Kali Linux comes with so many preconfigured and preloaded tools, it’s the Swiss Army knife of security professionals’ toolkits.
Professionals That Use Kali Linux
- Security Administrators – Security administrators are in charge of protecting the data and information of their organization. They examine their environment(s) using Kali Linux to make sure there are no readily apparent vulnerabilities.
- Network Administrators – Network administrators must keep their networks safe and effective. To audit their network, they employ Kali Linux. Kali Linux can identify rogue access points, for instance.
- Network Architects – The task of creating safe network environments falls to network architects. They audit their original designs using Kali Linux to make sure nothing was missed or configured incorrectly.
- Pen Testers – Pen testers are employed to analyze corporate environments; they use Kali Linux to audit environments and do reconnaissance.
- CISO – Chief Information Security Officers, or CISOs, can utilize Kali Linux to audit their environment internally and find out whether any malicious configurations or new apps have been installed.
- Forensic Engineers – In certain situations, a forensic engineer can carry out data recovery and discovery using Kali Linux’s “Forensic Mode.”
- White Hat Hackers – Like Pen Testers, White Hat Hackers utilize Kali Linux to audit and find potential vulnerabilities in an environment.
- Black Hat Hackers – Kali Linux is a tool that black hat hackers use to find and take advantage of vulnerabilities. Additionally, Kali Linux offers a wide variety of social engineering tools that a Black Hat Hacker could use to corrupt a company or an individual.
- Grey Hat Hackers – The middle class of hackers are known as “grey hat” hackers. They’ll use Kali Linux in the same ways as the first two mentioned.
- Computer Enthusiast – Although the phrase “computer enthusiast” is somewhat broad, anyone who is curious about computers or networking in general can use Kali Linux to learn more about common vulnerabilities, networking, and information technology.
Kali Linux Installation Methods
You can install Kali Linux in a few different ways:
Ways to Run Kali Linux:
- Directly on a PC or laptop – Kali Linux can be installed straight onto a PC or laptop by using a Kali ISO image. If you are familiar with Kali Linux and have a spare PC, this is the ideal method. Additionally, it is advised that you install Kali Linux straight onto a laptop with WiFi if you intend to perform any access point testing.
- Virtualized (VMware, Hyper-V, Oracle VirtualBox, Citrix) – Kali Linux may be readily integrated with the most widely used hypervisors and supports the majority of them. You can acquire pre-configured images from https://www.kali.org/, or you can manually install the operating system into your choice hypervisor using an ISO file.
- Cloud (Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure) – Given Kali Linux’s widespread use, images for the operating system are available from both AWS and Azure.
- USB Boot Disc – The ISO file for Kali Linux can be used to produce a boot disk that can be used for forensic analysis or to run Kali Linux on a computer without installing it.
- Windows 10 (App) – With Windows 10, Kali Linux may now be executed natively using the Command Line. As it’s currently in beta testing, not all functions are functional yet.
- Mac (Dual or Single boot) – On a Mac, Kali Linux can be set up as the primary operating system or as a backup. This system can be configured using Parallels or the Mac’s boot capabilities.
How To Install Kali Linux Using Virtual Box?
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Kali Linux and install it using Virtual Box:
The simplest and possibly most popular approach is to install Kali Linux and run it within Oracle VirtualBox.
With this method, you can experiment with the fully-featured Kali Linux in a fully isolated environment, all while keeping your current hardware. And best of all, it’s all free. You can use Oracle VirtualBox and Kali Linux for free.
It is assumed that you have already installed Oracle VirtualBox on your computer and enabled 64-bit virtualization through the BIOS to follow this Kali Linux tutorial.
Step 1) Go to https://www.kali.org/downloads/
By doing this, you can import an OVA image into VirtualBox.
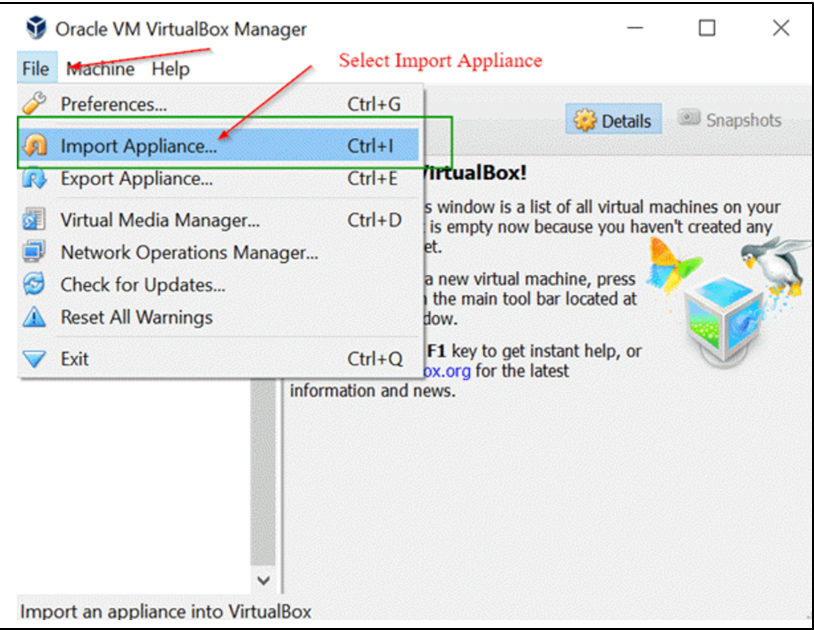
Step 2) Launch the Oracle VirtualBox application, then choose Import Appliance from the File menu.
File Menu -> Import Appliance
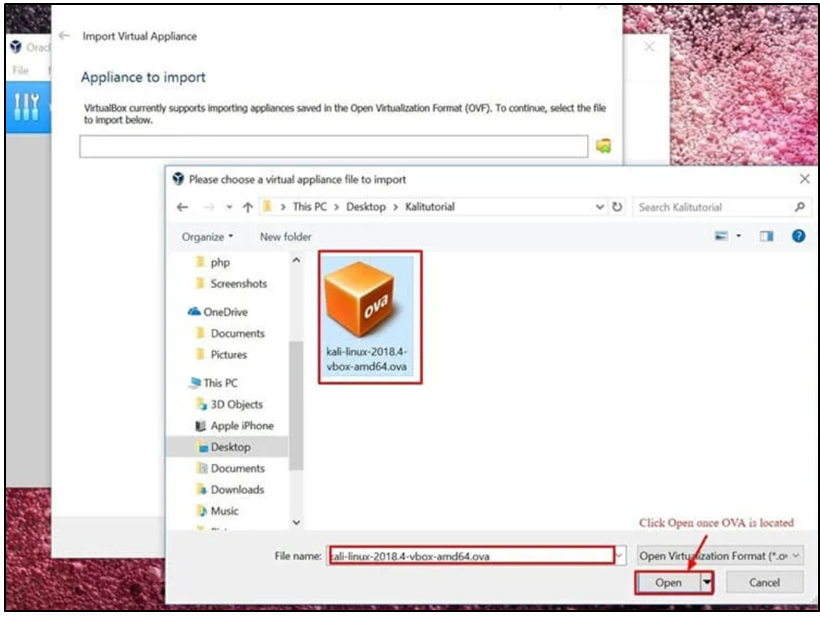
Step 3) On the “Appliance to Import” screen that appears next Click Open after navigating to the location of the OVA file that was downloaded.
Step 4) You will be brought back to the “Appliance to Import” screen after clicking “Open.” All you have to do is click Next.
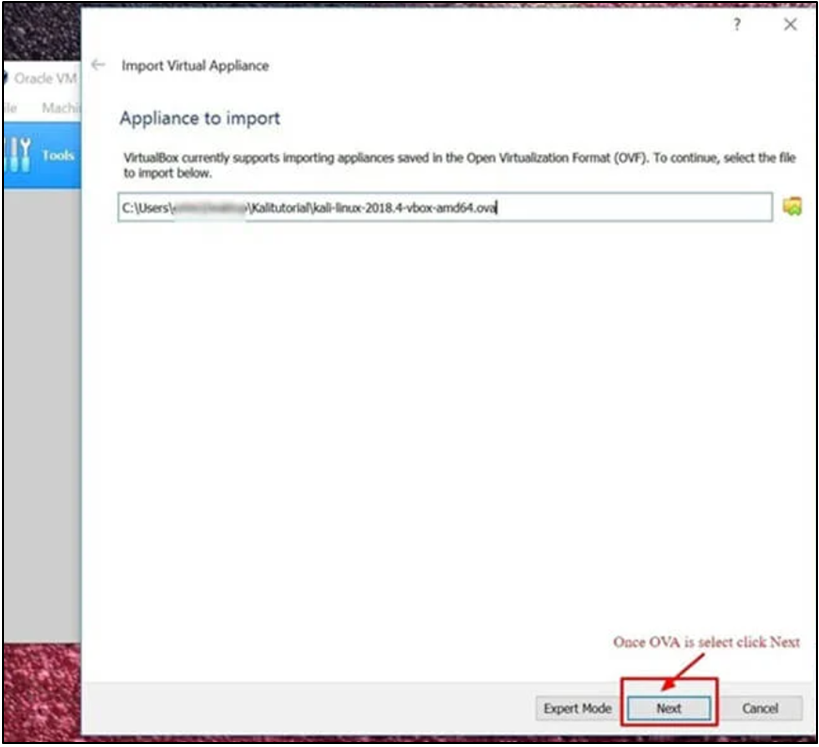
Step 5) Leaving the default settings on the “Appliance Settings” panel, which shows an overview of the system’s parameters, is OK. Click Import after taking note of the Virtual Machine’s location, as indicated in the screenshot below.
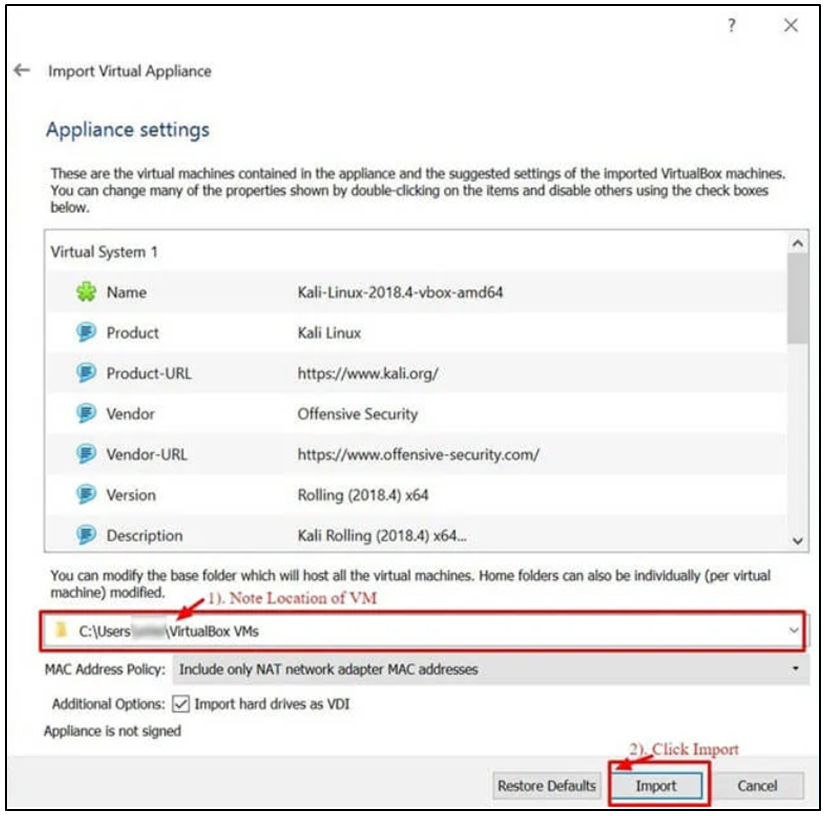
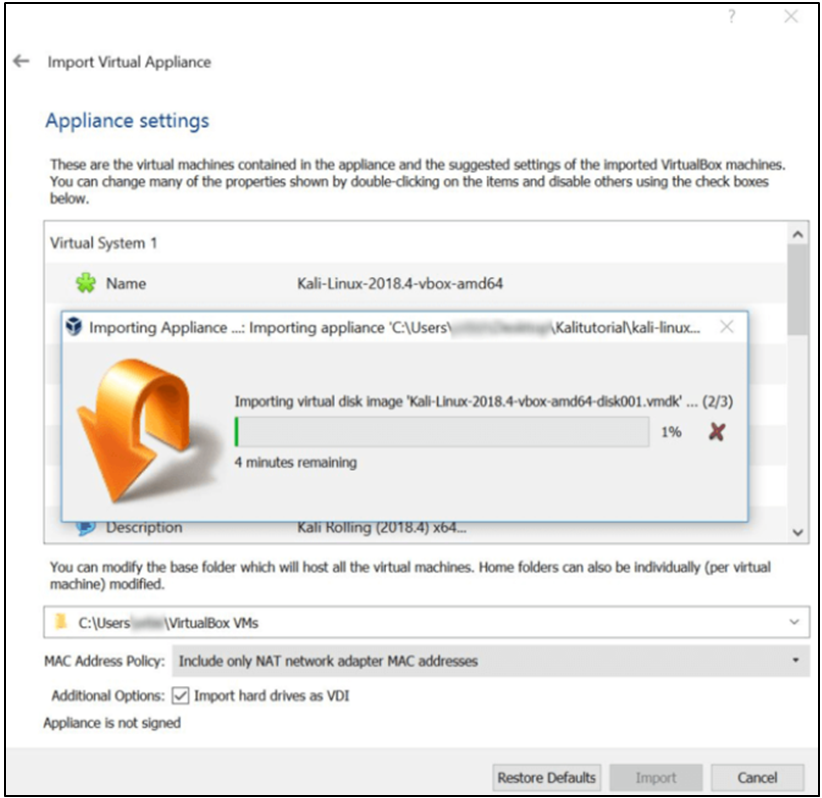
Step 6) This will import the Kali Linux OVA appliance into VirtualBox. It could take 5 to 10 minutes to finish this process.
Step 7) You’ve successfully installed Kali Linux on VirtualBox, congratulations. Now the Kali Linux virtual machine ought should appear in the VirtualBox Console. Next, we’ll examine Kali Linux and a few preliminary actions to do.
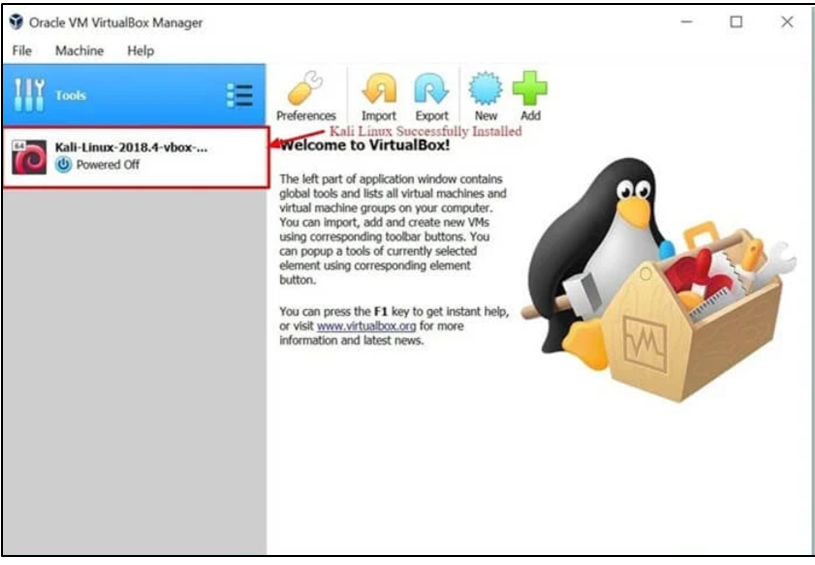
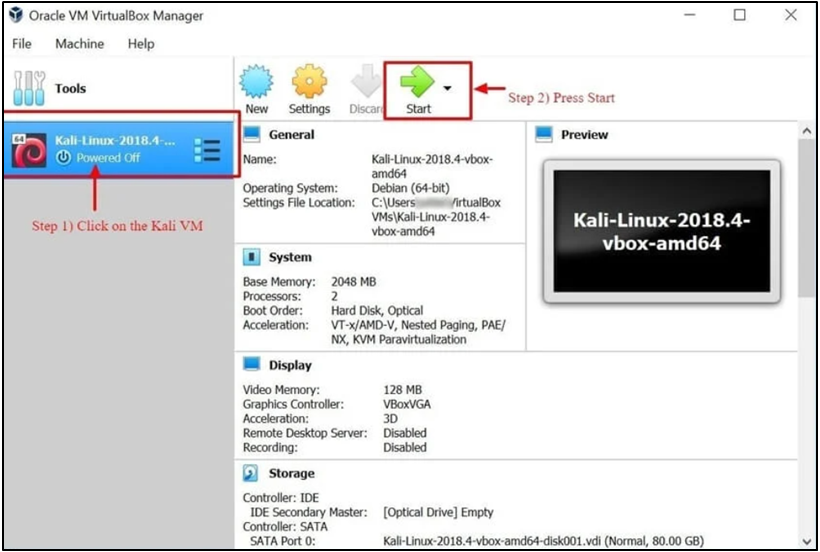
Step 8) To launch the Kali Linux operating system, click the Kali Linux virtual machine (VM) on the VirtualBox Dashboard, then select Start.
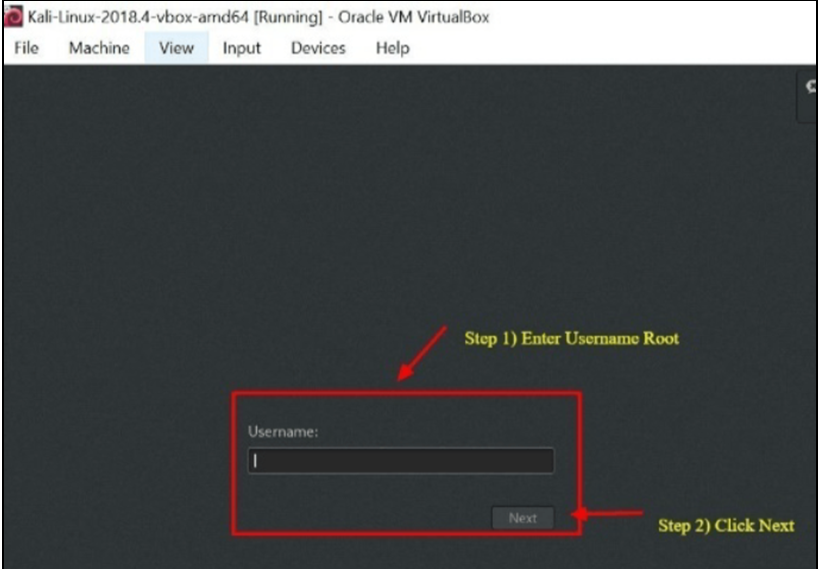
Step 9) Click Next after entering “Root” as the username on the login screen.
Step 10) As previously stated, click sign in after entering “toor” as the password.
The Kali Linux GUI Desktop will now appear on your screen. Congratulations! Your login to Kali Linux was successful.
Getting Started with Kali Linux GUI.
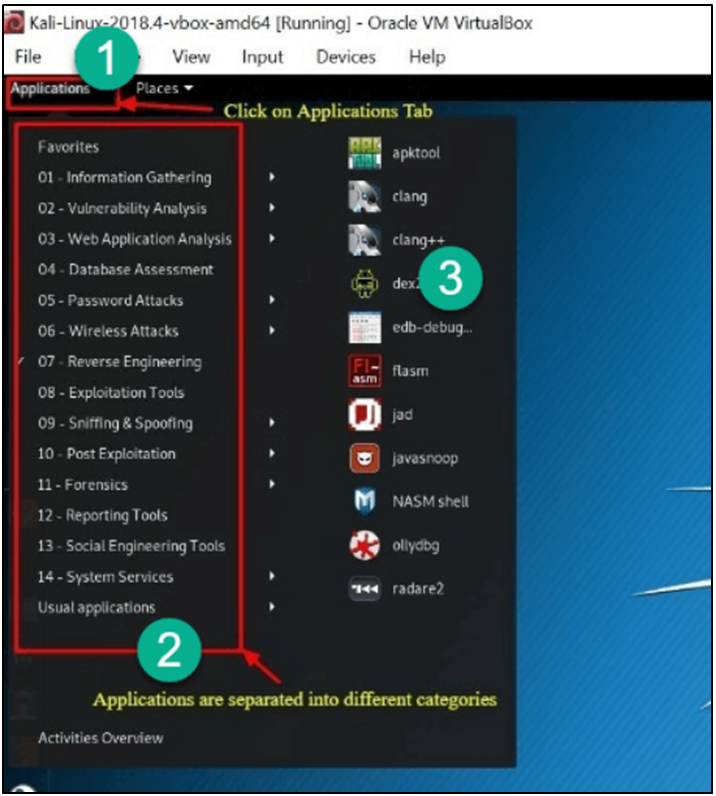
There are a few tabs on the Kali Desktop that you should first notice and get acquainted with. The Kali Linux Dock, Places Tab, and Applications Tab.
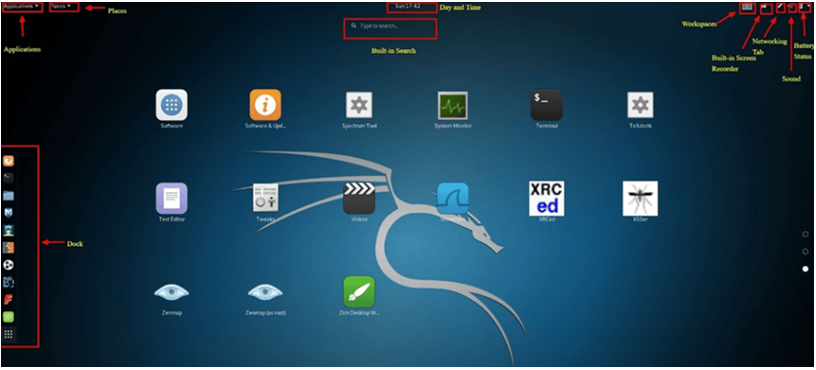
Applications Tab: Offers a Graphic Dropdown List of all Kali Linux’s pre-installed programs and utilities. Examining the Applications Tab is an excellent approach to learning about the Kali Linux Operating System and its enhanced features.
In this Kali Linux tutorial, we’ll talk about two programs: Nmap and Metasploit. The apps are categorized, which greatly facilitates the process of finding an application.
Accessing Applications
Step 1) Select the Applications Tab.
Step 2) Navigate to the specific category you want to learn more about.
Step 3) Select the application you want to launch by clicking on it.
Places Tab: As with any other GUI OS, like Windows or Mac, this tab provides quick access to your Folders, Pictures, and My Documents, which are crucial components. Locations in Kali Linux give an Operating System its essential accessibility.
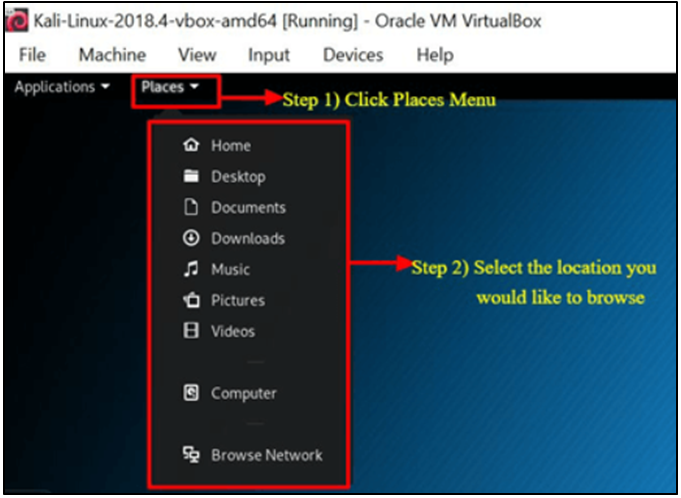
The Home, Desktop, Documents, Downloads, Music, Pictures, Videos, Computer, and Browse Network tabs are the ones that are present by default in the Places menu.
Accessing Places
Step 1) Select the Places Tab.
Step 2) Choose the location that you want to access.
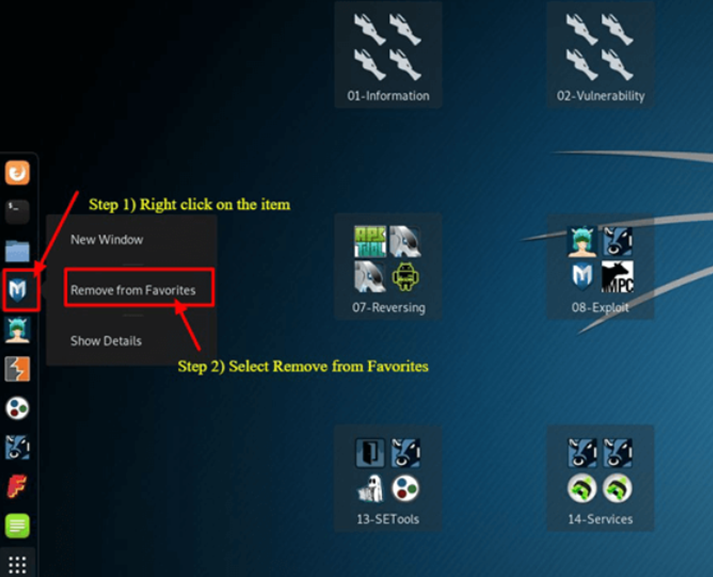
Dock For Kali Linux: Like the Task Bar in Microsoft Windows or the Dock on Apple Macs, the Kali Linux Dock offers fast access to frequently used or favorite apps. It’s simple to add or remove applications.
To Take Something Out of the Dock
Step 1) Press and Hold the Dock Item.
Step 2) Click “Remove From Favorites.”
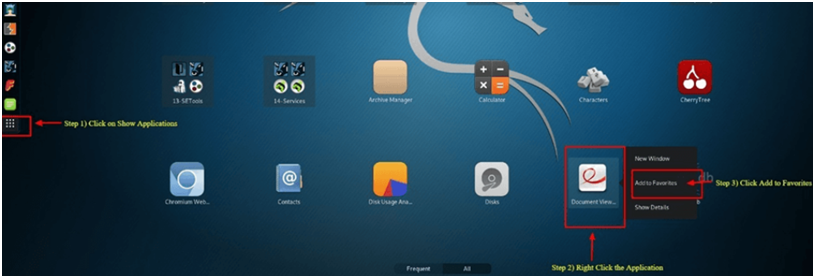
To Add Item to Dock
There are many similarities between adding and removing items from the Dock.
Step 1) Select the Show Applications icon located at the Dock’s bottom.
Step 2) Right-Click on Application
Step 3) Select Add to Favorites
When finished, the item will appear in the Dock.
Because of its many additional special characteristics, Kali Linux is the operating system of choice for both hackers and security engineers. It is not possible to cover them all in this Kali Linux hacking guide but feel free to experiment with the many buttons that are visible on the desktop.
What is Nmap?
Network Mapper, also referred to as Nmap for short, is an open-source, free tool for vulnerability scanning and network discovery. Nmap is a tool used by security experts to find devices that are operating in their settings.
Nmap can also expose a potential security issue by revealing the services and ports that each host is serving. To put it simply, think of Nmap as a ping on steroids. Nmap will be more beneficial to you as your technical abilities increase.
With Nmap, you can easily keep an eye on a single host or a large network with hundreds or even thousands of devices and subnets. Although Nmap’s functionality has changed over time, at its foundation, it is still a port-scanning program that obtains data by transmitting raw packets to a host machine.
After that, Nmap waits for a response before determining whether a port is filtered, open, or closed. The basic Nmap scan, which checks the first 1000 TCP ports, is the first scan you should be familiar with. It will indicate if a port is open, closed, or filtered if it finds one that is listening.
Filtered indicates that there is probably a firewall in place that is altering the traffic on that specific port. The Nmap commands that can be used to do the default scan are listed below.
Nmap Target Selection
| Scan a single IP | nmap 192.168.1.1 |
| Scan a host | nmap www.testnetwork.com |
| Scan a range of IPs | nmap 192.168.1.1-20 |
| Scan a subnet | nmap 192.168.1.0/24 |
| Scan targets from a text file | nmap -iL list-of-ipaddresses.txt |
How to Perform a Basic Nmap Scan on Kali Linux?
Here are steps on how to execute a basic Nmap scan in Kali Linux. You can scan a single IP address, a DNS name, a range of IP addresses, Subnets, and even text files with Nmap as seen above. We are going to scan the localhost IP address in this example.
Step 1) Select the Terminal tab, the second one, from the Dock Menu.
Step 2) Once the Terminal window has opened, type the command ifconfig to get your Kali Linux system’s local IP address. The local IP address in this case is 10.0.2.15.
Step 3) Take note of the IP address that is local.
Step 4) Enter nmap 10.0.2.15 in the same terminal window to scan the first 1000 ports on the localhost. Since this is a base setup, there shouldn’t be any open ports.
Step 5) Review results.
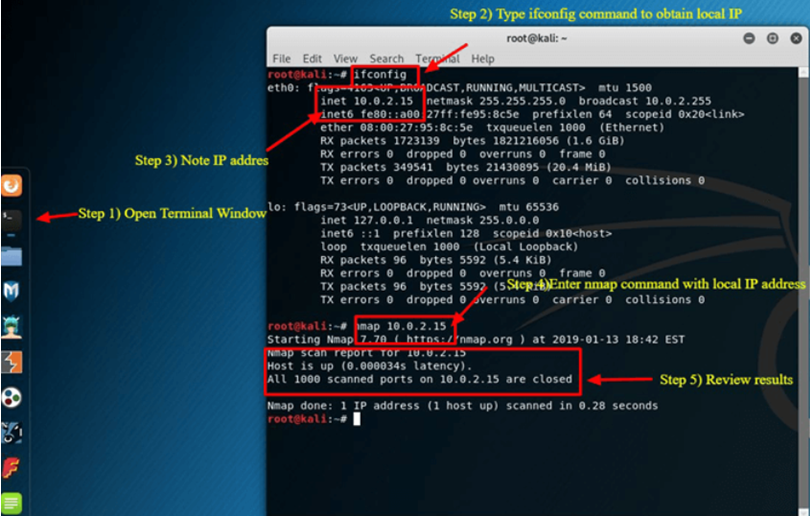
Nmap only searches the top 1000 ports by default. You could easily add -p- to the preceding command to scan all 65535 ports if necessary.
| Nmap 10.0.2.15 -p- |
Nmap OS Scan
Nmap’s capability to identify the host system’s operating system is another fundamental yet practical function. Since Kali Linux is by default secure, the host system—on which Oracle’s VirtualBox is installed—will be utilized as an example in this instance. The Windows 10 Surface is the host system. 10.28.2.26 is the IP address of the host system.
Enter the following nmap command into the Terminal window:
| nmap 10.28.2.26 – A |
Review results
By using -A, nmap is instructed to attempt to identify the operating system in addition to conducting a port scan.
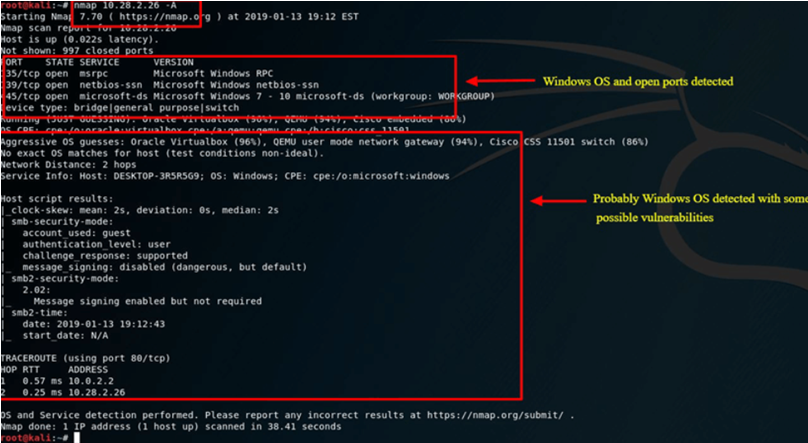
Nmap is an essential tool for every security professional’s toolkit. To view other Nmap commands and options, use the nmap -h command.
What is Metasploit?
An open-source project called the Metasploit Framework offers the public a resource for studying security flaws and creating code that enables network intrusions and vulnerability detection for security experts.
Rapid 7 just acquired Metasploit (https://www.metasploit.com). On Kali Linux, Metasploit’s community edition is still accessible, though. The most popular penetration tool in the world is without a doubt Metasploit.
When utilizing Metasploit, exercise caution because there are situations where scanning a network or environment that is not yours could be illegal. You will learn how to launch Metasploit and perform a basic scan on Kali Linux in this tutorial on Metasploit for Kali Linux.
Although Metasploit is regarded as an advanced tool and will take some time to become proficient with, if you know how to use it, it’s a really useful tool.
Metasploit and Nmap
Nmap is something we can use within Metasploit. In this instance, you will discover how to use the Nmap tool that we recently learned about to scan your local VirtualBox network from Metasploit.
Step 1) Choose Metasploit after swiping down to 08-Exploitation Tools on the Applications Tab.
Step 2) This is Metasploit; a terminal box will appear with the MSF dialog box shown.
Step 3) Put the following command in.
| db_nmap -V -sV 10.0.2.15/24 |
(Make sure to enter your local IP address in place of 10.0.2.15.)
Here:
db_ stands for the database
-V Stands for verbose mode
-sV stands for service version detection.
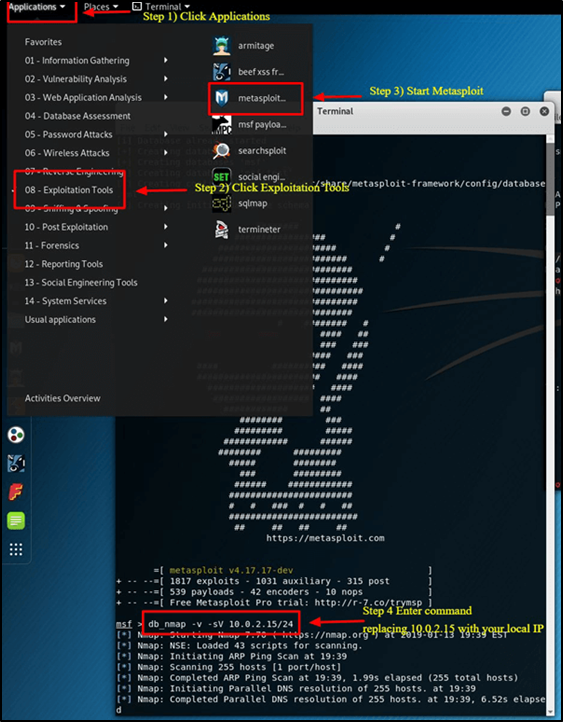
Metasploit Exploit Utility
With its capabilities and versatility, Metasploit is incredibly versatile. Exploiting vulnerabilities is a popular usage for Metasploit. We’ll walk through how to review a few exploits and attempt to hack a Windows 7 machine below.
Step 1) Go into the terminal window and type Hosts -R, assuming Metasploit is still open. This updates the Metasploit database with the hosts that were recently found.
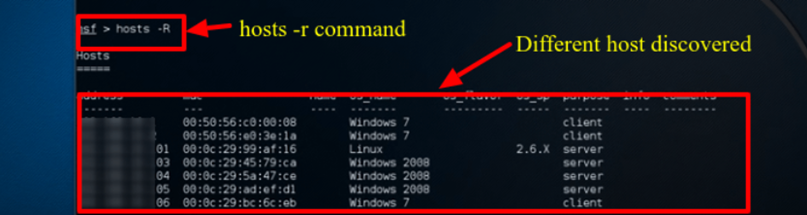
Step 2) Enter “show exploits” to view an extensive list of all the exploits that Metasploit has to offer.
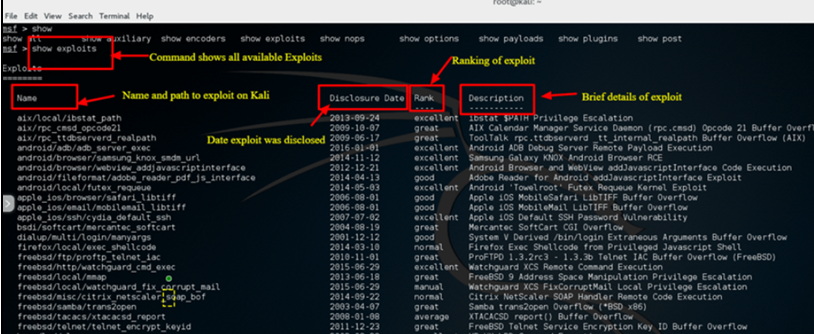
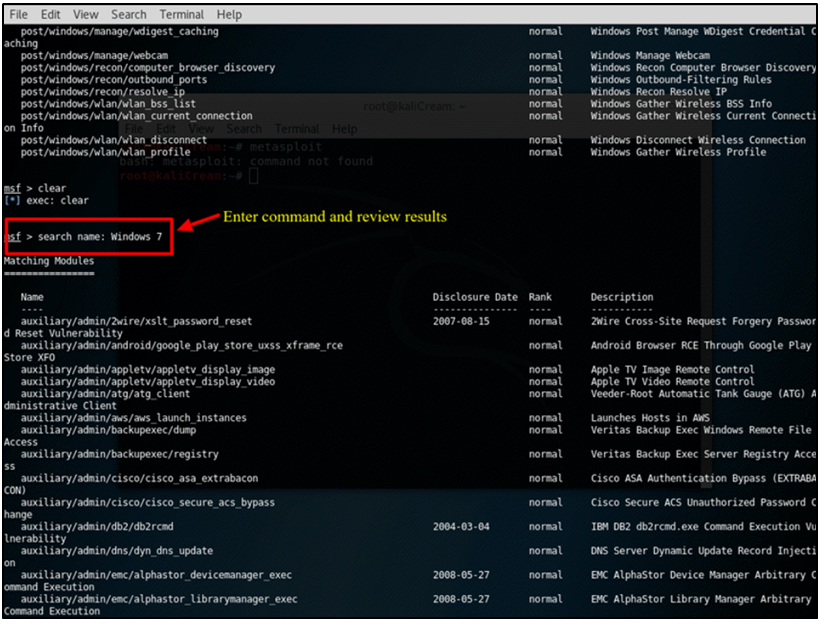
Step 3) Try using the following command to filter the list now: We’ll attempt to exploit a Windows 7 machine in this example. The search name for this command is Windows 7, and it looks for exploits that explicitly include Windows 7.
To satisfy your criteria, you may need to adjust the search parameters based on your environment. You will need to modify the search parameter to correspond with the sort of machine you have, for instance, if it’s a Mac or another Linux machine.
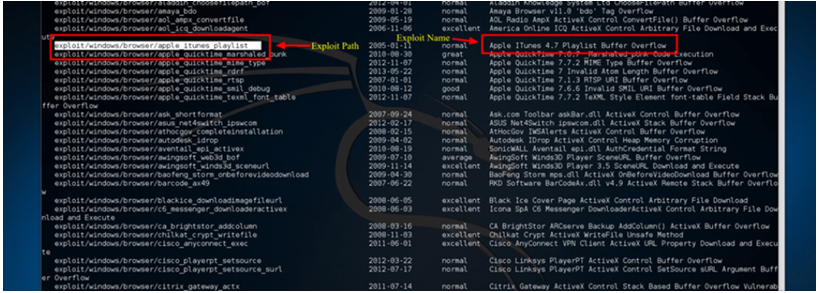
Step 4) We’ll use an Apple iTunes Vulnerability that was found on the list for this tutorial. We have to enter the entire path shown in the list to use the exploit: Take use of exploit/windows/browse/apple_itunes_playlist.
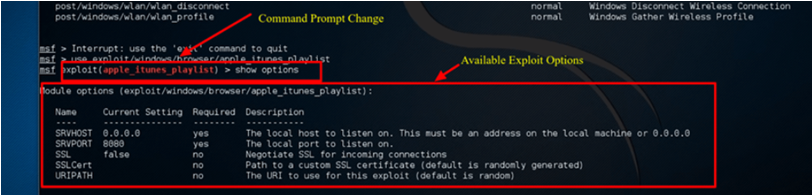
Step 5) The command prompt will alter to show the exploit name followed by > if the exploit is successful, as seen in the screenshot below.
Step 6) To see the options available to the exploit, type show options. Naturally, each exploit will have a unique set of possibilities.
Summary
Security administrators, black hat hackers, and other professionals utilize Kali Linux, an incredible operating system, extensively. It’s an operating system that everyone in the IT sector and computer fans should be familiar with due to its extensive use, reliability, and ease of use.
Securing an organization’s IT infrastructure can be greatly aided by utilizing simply the two apps covered in this course. Although Nmap and Metasploit are available on other platforms, Kali Linux is the preferred operating system for assessing and testing network security due to its pre-installed configuration and ease of use.
Kali Linux should only be used in network environments that you control or have authorization to test, as was previously said. Use caution when using it. Since certain utilities could result in data loss or damage.
About The Author
Suraj Koli is a content specialist with expertise in Cybersecurity and B2B Domains. He has provided his skills for the News4Hackers Blog and Craw Security. Moreover, he has written content for various sectors Business, Law, Food & Beverage, Entertainment, and many others. Koli established his center of the field in a very amazing scenario. Simply said, he started his career selling products, where he enhanced his skills in understanding the product and the point of view of clients from the customer’s perspective, which simplified his journey in the long run. It makes him an interesting personality among other writers. Currently, he is a regular writer at Craw Security.
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE









